Pallet optimization is the practice of carefully stacking, wrapping, and labeling products on a pallet so they use space efficiently. The goal is to lower shipping costs based on package size. With the right techniques, you can prepare your pallets to help minimize DIM weight on your shipment.
Effectively packed goods fit better on trucks and help shipments move faster. Good pallet optimization makes shipping smoother at every step, from loading in the warehouse to delivery at the final destination. When done right, pallet optimization is an easy way to save money and improve efficiency in the shipping process.
What are DIM Weight Charges
Dimensional Weight Charges (DIM Weight) consider the density and actual weight of the parcel as well as its size. Shippers need to know how much room a pallet takes up on a trailer, and using DIM weight charges help price it out accordingly.

How DIM Weight Works
The calculation compares two weights:
- Actual weight: What the package physically weighs
- Dimensional weight: Calculated by multiplying length × width × height, then dividing by a DIM factor (typically 139 for domestic shipments, 166 for international)
The shipping cost is based on whichever weight is greater.
How Carriers Set DIM Factors
Carriers determine DIM factors based on a number of data points. This includes average cargo density in their transportation network, operational costs and efficiency targets, market competition, and the type of service, such as ground vs. air.
The DIM factor essentially represents how many cubic inches equal one pound in the carrier’s pricing model. A lower DIM factor (like 139) makes DIM weight higher, resulting in higher costs for bulky, lightweight packages.
Different carriers may use slightly different factors, and they can change these numbers as part of their pricing strategy.
Why DIM Weight Matters
By packaging your shipments efficiently, you will be able to reduce DIM weight and save on shipping. Companies see immediate savings when shipping packages with effective space-saving measures. Also, it could improve delivery times by making the shipment easier and faster to handle.
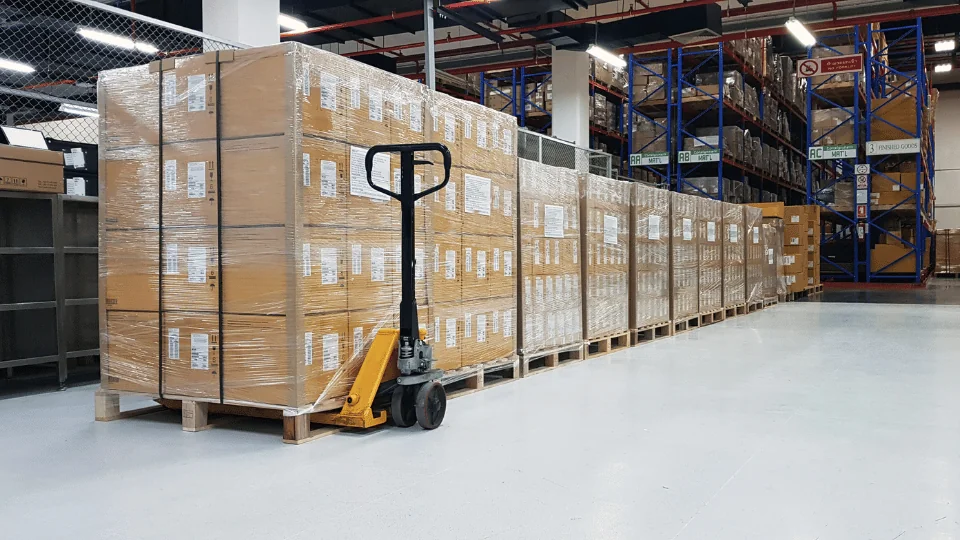
Stacking Pallets for Optimization
Stacking is the foundation of pallet optimization. How you build your pallet matters a lot in how safely goods are shipped and how efficiently they move through the supply chain. A well-stacked pallet is easier to wrap, label, and transport without issues.
Solid stacking is the practice of arranging boxes in a formation that protects the shipment while making the most of the pallet’s footprint. It involves placing heavier items at the bottom. Each layer should be aligned evenly and avoid overhang or empty gaps that could cause the load to shift.
Make the most of the pallet’s surface area without letting any items hang over the edge. A tight, well-aligned footprint helps the load stay stable, simplifies loading into trailers or containers, and reduces the chance of extra handling fees.
Aim to build in straight lines with a uniform shape. Keeping the stack cubic makes it easier to wrap and label, and also helps avoid excess dimensional weight charges. Misaligned or overhanging boxes can lead to damage and may prompt carriers to remeasure the pallet, which could increase your shipping costs.
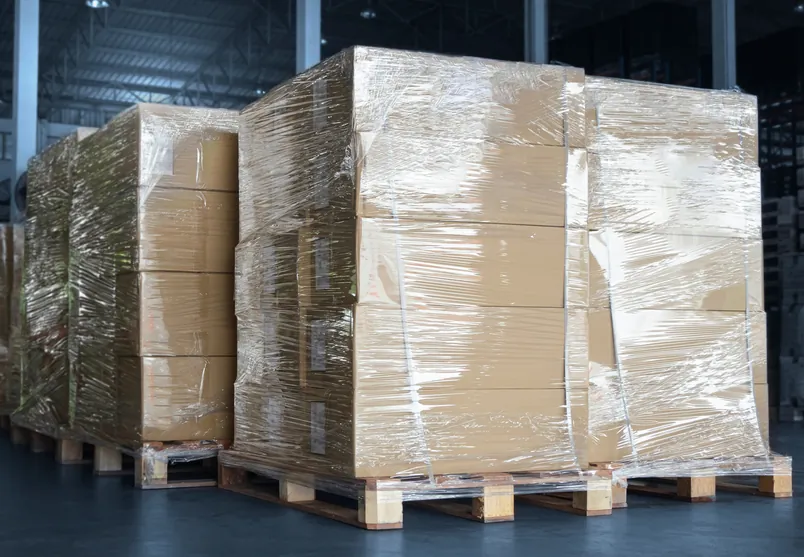
Wrapping Pallets
Wrapping pallets properly helps lower DIM weight charges by keeping the load compact, stable, and easy to measure. When a pallet is tightly and evenly wrapped, it prevents the boxes from shifting or bulging out, which can increase the measured size of the shipment. Proper wrapping ensures the pallet stays within expected dimensions, helping you avoid surprise fees and keeping your shipping costs lower.
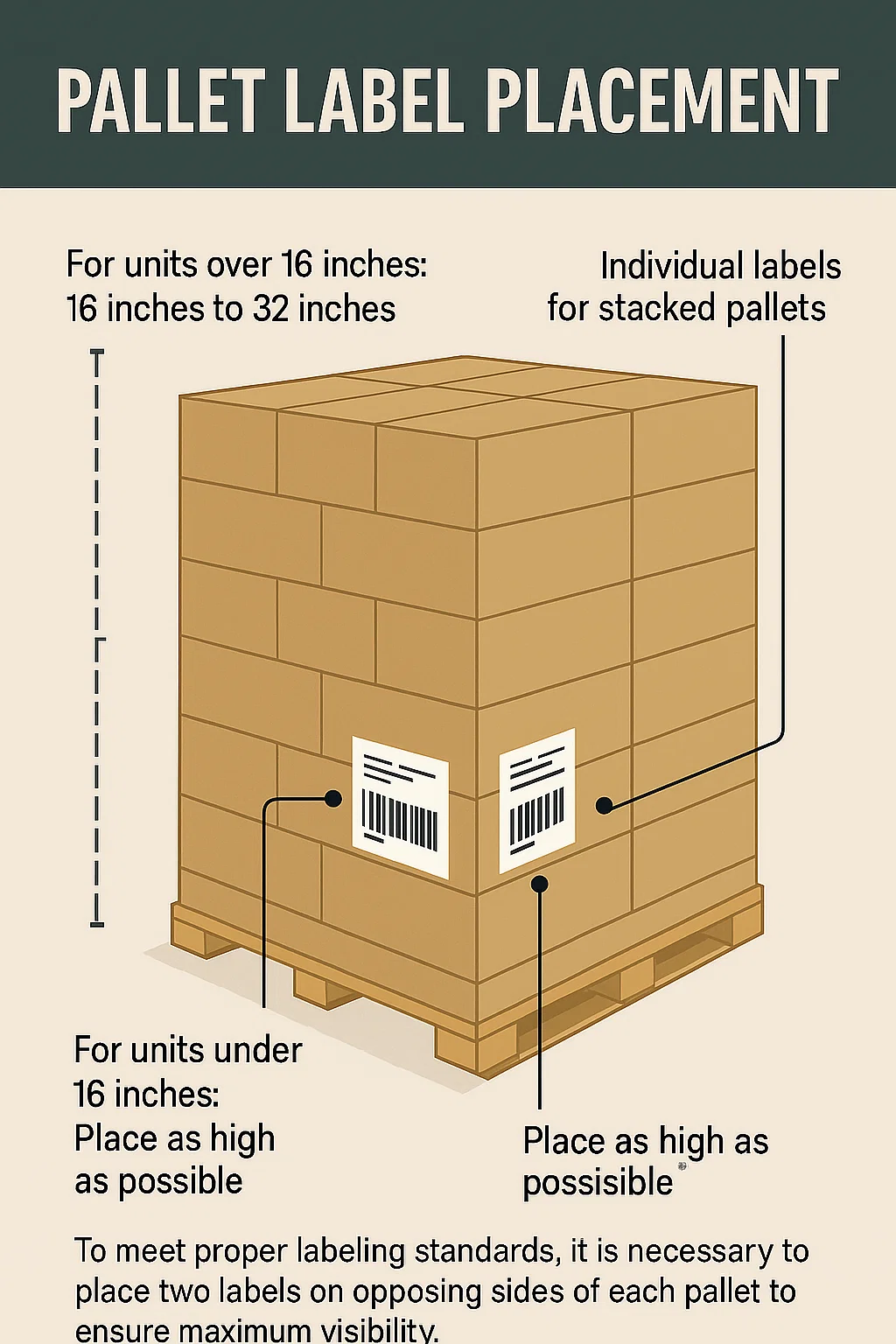
Labeling Pallets
Correctly identifying the dimensions of the pallets helps streamline the shipping process. By having accurate information on the labels, you avoid having the size of the package overestimated and being overcharged. Be sure to use best practices when labeling pallets, such as having the labels at eye level, if applicable, as well as being placed on two sides for maximum visibility.
Standardizing Pallet Sizes
The most common pallet size in North America is the 48 x 40-inch pallet, often referred to as the “GMA pallet” (Grocery Manufacturers Association pallet). This pallet size accounts for around 26-30% of all pallets used and is widely adopted across various industries, including grocery, retail, manufacturing, and distribution.
Using the same pallet size across shipments makes shipping and handling easier, faster, and more cost-effective. These pallets work well with common tools like forklifts and pallet jacks, which speed up loading and unloading while reducing the risk of damage or accidents. Because their dimensions are consistent, they fit neatly into trailers, containers, and warehouse racks, allowing businesses to use space more efficiently and avoid delays.
Standardized pallets are the most widely available and usually more affordable than custom-sized options. Uniform sizing helps secure cargo better and prevents it from shifting during transport.
In some cases, pallet optimization can even help your shipment qualify for faster service levels or earlier trailer loading. Smaller, more compact packages are simpler to stack, scan, and load onto trucks or aircraft. This speeds up sorting and reduces the chance of delays.
Pallet Optimization for Lowered Shipping Costs
The right approach to pallet optimization includes stacking with stability, wrapping with care, labeling with precision, and standardizing sizes. These techniques can make a big difference in both cost and performance. When every inch counts, optimizing your pallets isn’t just about saving space. It’s about delivering better results across your entire shipping operation.
Not only does pallet optimization help reduce DIM weight and avoid extra fees, but it also improves handling efficiency. As a result, shipments arrive safely and on time with reduced costs.